Introduction to Counterpoint
Part I - Doctrine of Affections
The doctrine of the affections, also known as the doctrine of affects, doctrine of the passions, theory of the affects, or by the German term Affektenlehre (after the German Affekt; plural Affekte) was a theory in musical aesthetics popular in the Baroque era (1600–1750). It derived from ancient theories of rhetoric and oratory (Buelow 2001), and was widely accepted by late-Baroque theorists and composers. The essential idea is that just one unified and "rationalized" Affekt should be aimed at by any single piece or movement of music, and that to attempt more was to risk confusion and disorder.
According to one version of the theory there are three pairs of opposing emotions that make six "affects" all together: love/hate, joy/sorrow, wonder/desire. Another authority also mentions sadness, anger, and jealousy (Buelow 2001).
Lorenzo Giacomini (1552–1598) in his Orationi e discorsi (1597) defined an affection as "a spiritual movement or operation of the mind in which it is attracted or repelled by an object it has come to know as a result of an imbalance in the animal spirits and vapours that flow continually throughout the body" (Giacomini 1597,).
The doctrine fell out of use in the Classical era, when composers and theorists began to find it excessively mechanical and unnatural.
"Affections are not the same as emotions; however, they are a spiritual movement of the mind" (Palisca 1991, 3).
A prominent Baroque proponent of the Doctrine of the Affections was Johann Mattheson (Poultney 1996, 107).
Part II - Texture
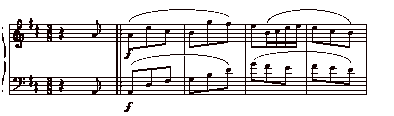
The texture is countrapuntal. Meaning that There is a melody and one or more counter-melodies.
Fig.1 melody and counter-melody
As seen here, the treble clef has the melody and the Bass clef has the counter-melody. The idea of two or more voices that move at different intervals of time is counterpoint.