Lesson 44 - Non-Tertian Harmonic Techniques
Part I - Quartal Harmony
Tonal music is said to be based on the principles of Tertian Harmony, or chords built in thirds. It is also posible to create harmonic systems that use other intervals as their basis. Quartal harmony is built on the interval of a fourth. That is the trichords are stacked in fourths.
Quartal trichords are considered to be in root position when all of the consecutive intervals are fourths. Notice that, in each chord, the outer interval is a 7th. When the trichords are inverted, the outer interval becomes a 5th.
Paul Hindemith is one of the most important composers to work in the realm of quartal harmony. He wrote many pieces for four part harmony (SATB) using chords stacked in fourths. Hindemith showed that it is possible to convey the sense of a tonic using quartal harmony. In his piece "A Swan," in measure five, the final resting chord, although it is a quartal trichord, can be considered 'tonic.'
Part II - clusters and Secundal Harmony
Sucundal harmony can be defined as that which the chords are built on and stacked in seconds. Bartók used this technique extensively in many of his works. Most famously Mikrokosmos. In Book VI, #144 in particular is called "Minor Seconds, Major Sevenths." The seconds and sevenths dominate the entire texture of this particular composition.
A parallel technique to secundal harmony is clusters:
The example in the treble clef shows a cluster where every note is notated. The example in the bass clef show an alternate notation to the cluster on the right would be the example on the left.
A good example of secundal harmony is in Charles Ives', "Hawthorne." Also, Henry Cowell's, "Tiger"
Part III - Microtones and Sound Mass
Inspired by the clusters of secundal harmony, some composers took it one step further and notated for every note within the range of an instrument.
This included notes between the normal half step. These notes are called microtones. A microtone is defined as any interval smaller than a second.
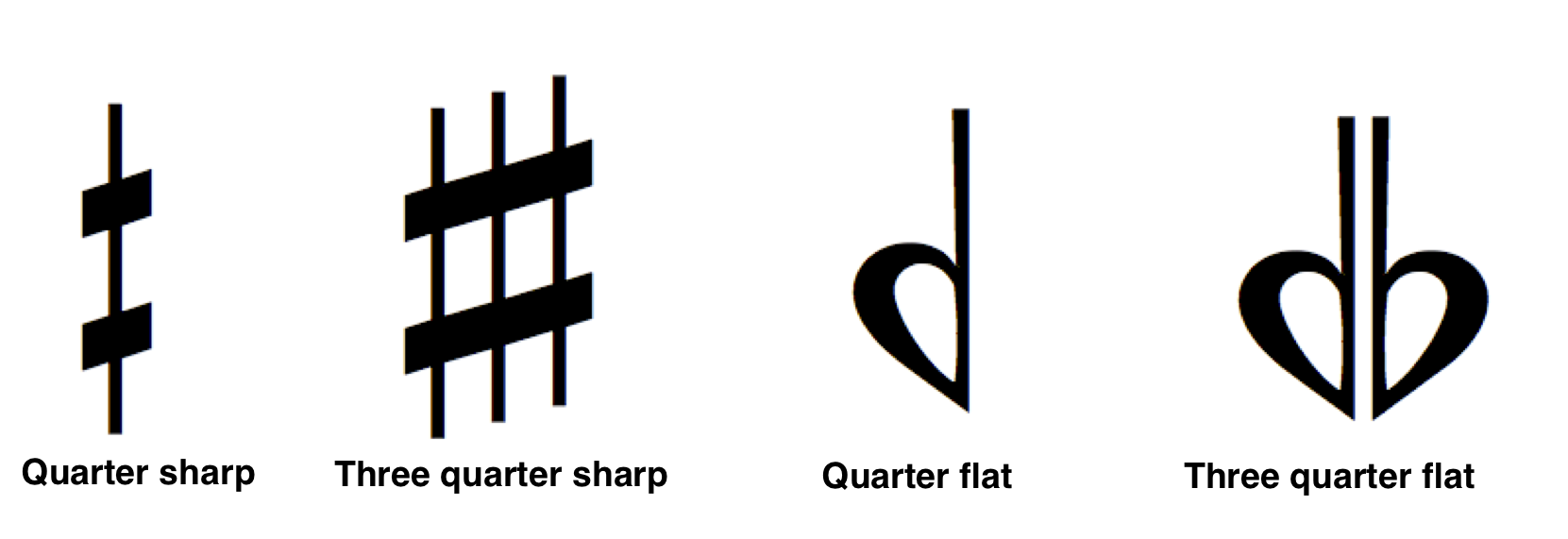
The string family is used most often to achieve microtones. One way to notate microtones is with the use of quarter sharps and flats.
THese are used to notate an interval smaller than a half step.